
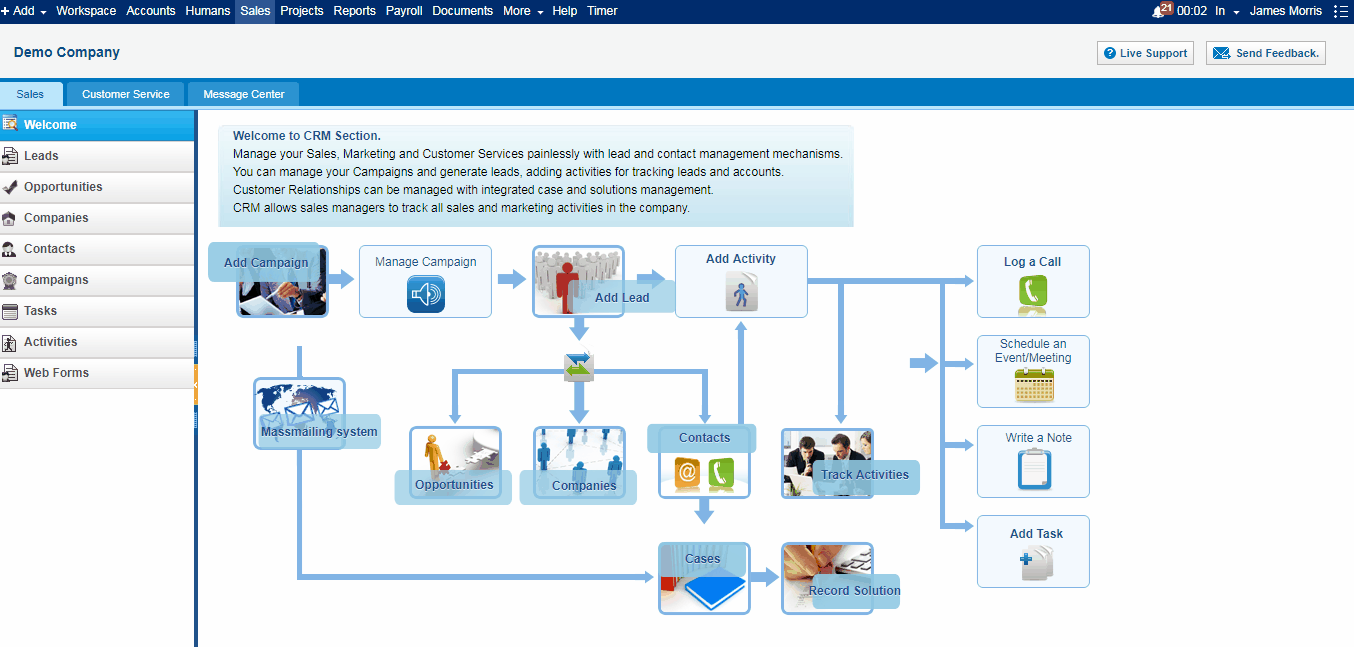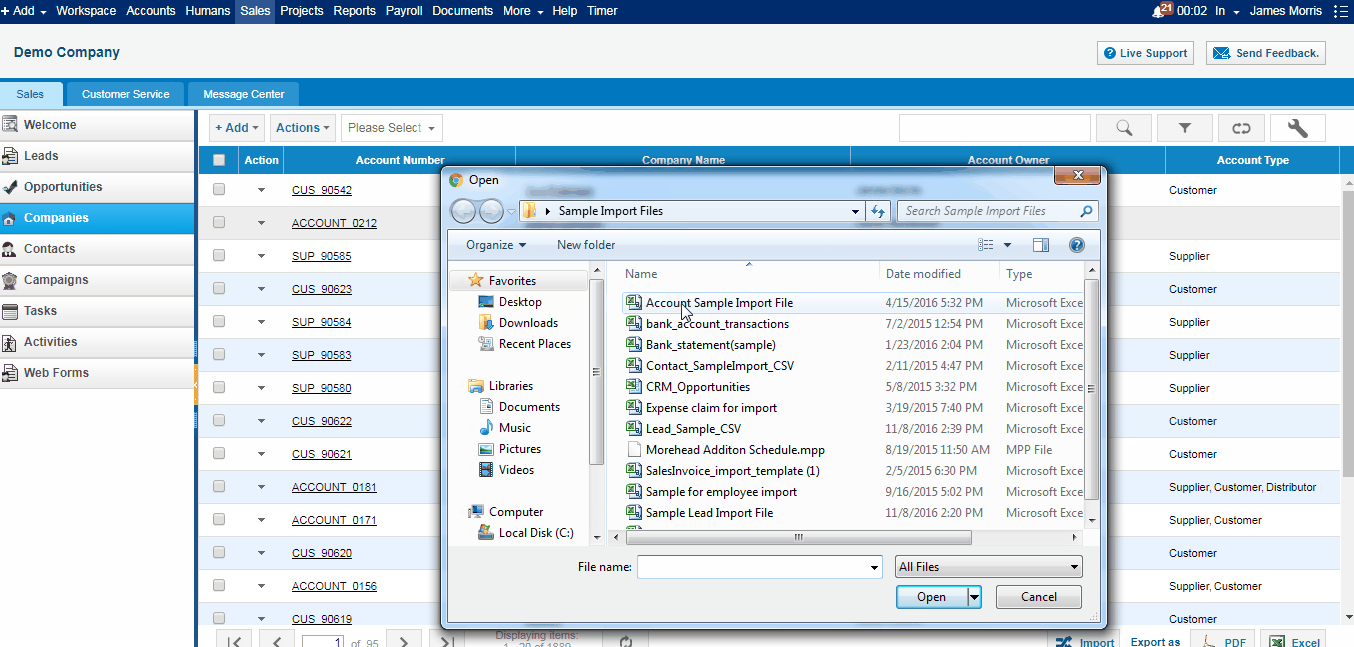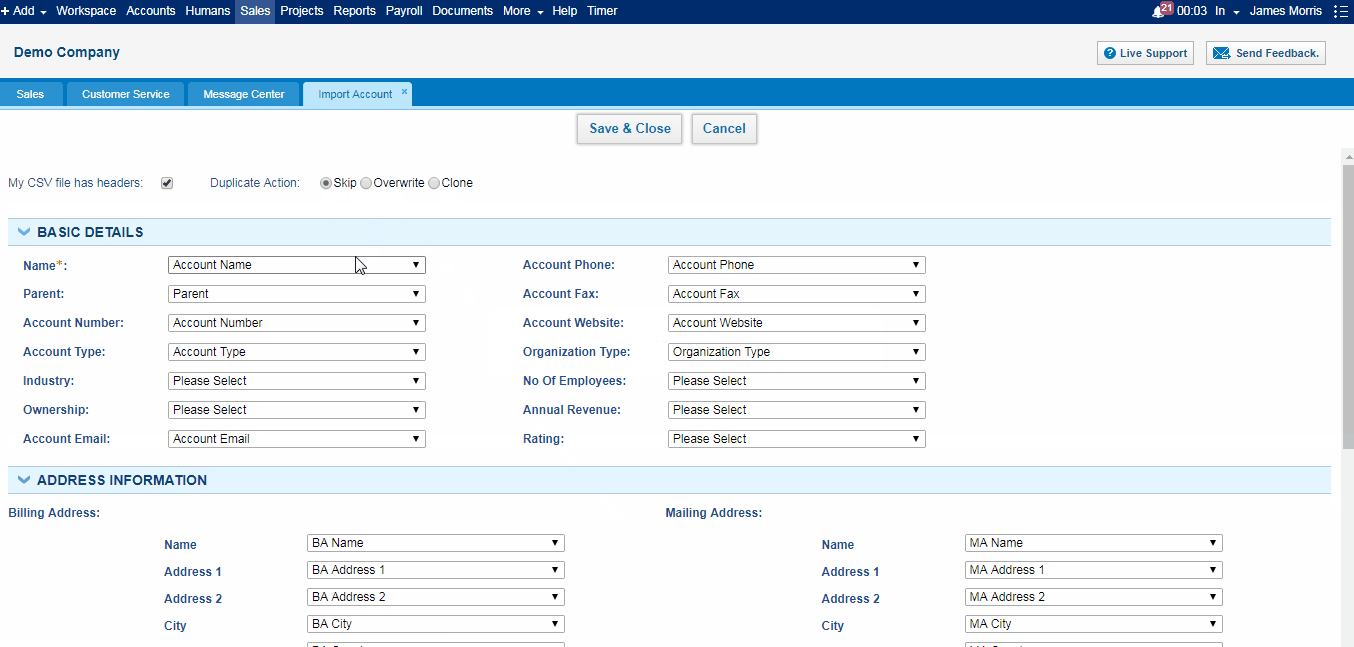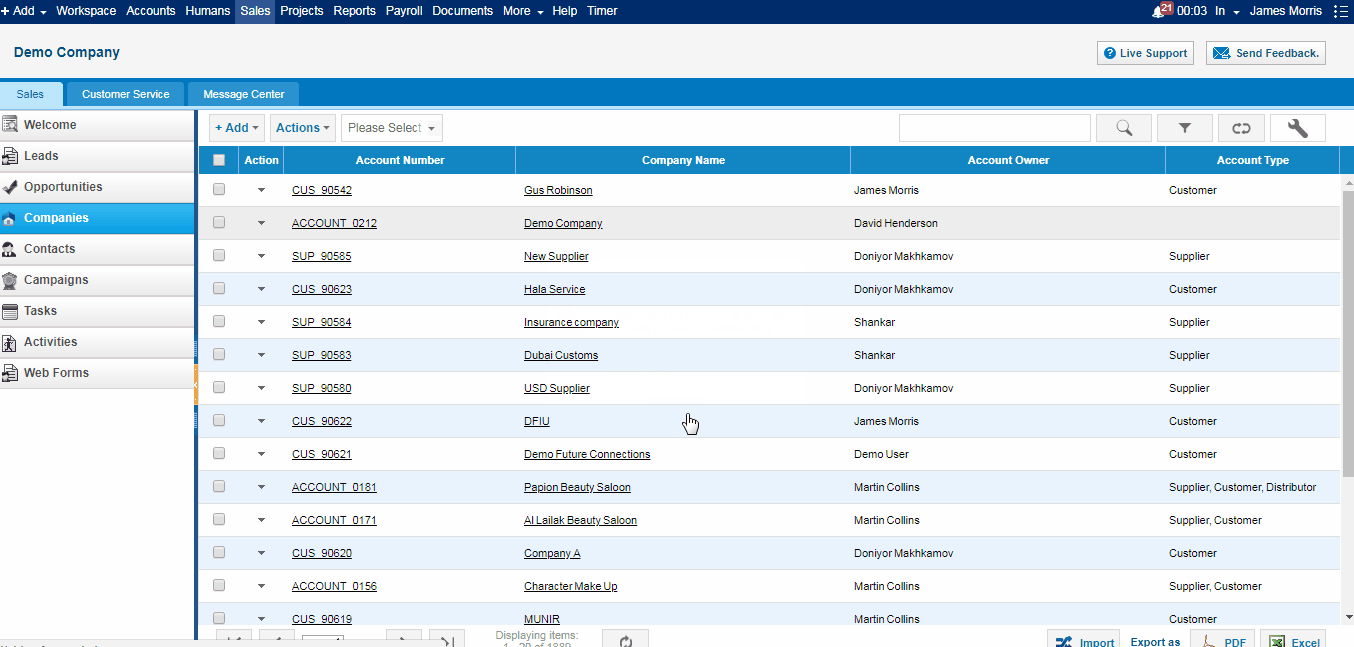
Imports of copper, a proxy for global growth, and natural gas were also down in the same period. Other recent data also showed South Korean exports to China, a leading indicator of China’s imports, were down 26.5% in April, continuing 10 consecutive months of decline.Ĭhina’s coal imports fell in April from a 15-month high in the prior month, snapping back as demand weakens in Asian giant. Yang Wenbin/Xinhua/Getty ImagesĬhina may have to bail out one of its poorest provinces
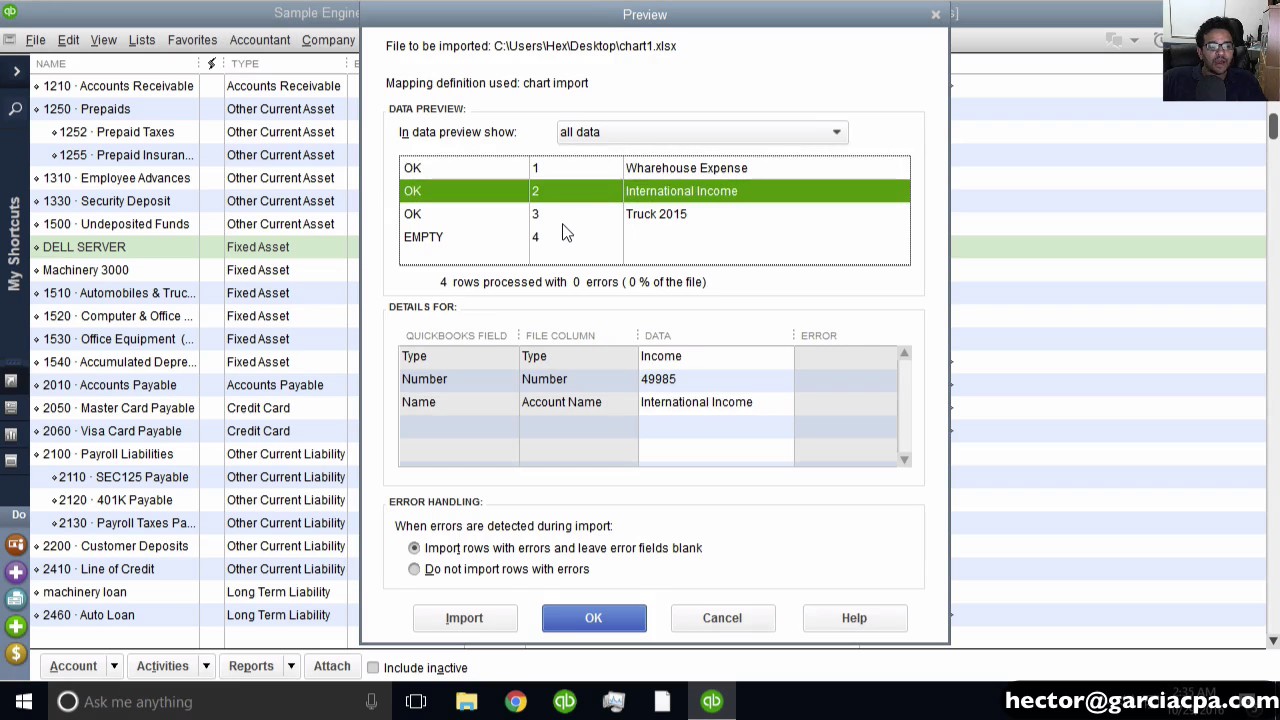
Guizhou government has borrowed heavily to fund its infrastructure spending. It's one of the tallest bridges in the world. This aerial photo taken on Apshows the Pingtang grand bridge on the expressway linking Pingtang and Luodian in southwest China's Guizhou Province. The region is China’s largest export partner. Shipments growth to ASEAN, a block of Southeast Asian countries, slowed to 4.5% in April from 35.4% last month. The downturn in imports suggests the world economy won’t be able to count much on China’s domestic engine of growth, and as the nation re-exports some of its imports, it also reinforces the extent of weakness in some of its major trading partner economies.Ī 15.3% drop in the import of semiconductors indicate the scale of the demand-pullback in the re-export market for such parts.Īnalysts say the sharp global monetary policy tightening campaign of the past 12-18 months and recent Western banking stress remain concerns for revival prospects of both China and worldwide. Hong Kong’s Hang Seng Index was down 1.11% in the early afternoon while China’s blue chip CSI300 Index was 0.26% weaker, after climbing 0.5% before the lunch break. The data appeared to push Hong Kong and mainland Chinese stocks lower, although global factors were also at play. “Given the gloomy outlook for external demand, we think exports will decline further before bottoming out later this year,” said Zichun Huang, China economist at Capital Economics in a note. The sharp deterioration in last month’s trade flows will only renew worries about the state of external demand and risks posed to the domestic economy, especially given the frail recovery from a year earlier when inbound and outbound shipments were severely disrupted by China’s Covid-19 restrictions.

One in 5 young people in Chinese cities are out of work. People attend a job fair in China's southwestern city of Chongqing on April 11, 2023. Government officials have repeatedly warned of a “severe” and “complicated” external environment in the wake of mounting recession risks for many of China’s key trading partners. “While China’s post-Covid rebound has been swift and sharp, it has been largely self-contained and not felt by the rest of the world,” he added. “At the beginning of this year, one would assume that imports will easily surpass 2022 levels following the reopening, but that hasn’t been the case,” said Xu Tianchen, an economist at the Economist Intelligence Unit. Inbound shipments to the world’s second-largest economy fell 7.9% year on year in April, extending the 1.4% decline seen a month earlier, while exports grew 8.5%, easing from the 14.8% surge in March, customs data showed on Tuesday.Įconomists in a Reuters poll had predicted no growth in imports and an 8.0% increase in exports. China’s imports contracted sharply in April, while exports rose at a slower pace, reinforcing signs of feeble domestic demand despite the lifting of Covid curbs and heaping pressure on an economy already struggling in the face of cooling global growth.Ĭhina’s economy grew faster than expected in the first quarter thanks to robust services consumption, but factory output has lagged and the latest trade numbers point to a long road to regaining the pre-pandemic momentum at home.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
